





高中英语人教版 (2019)必修 第一册Welcome unit评课ppt课件
展开
人教版高中英语必修一
Welcome Unit 第三课时 教学设计
课题 | Welcome Unit 第三课时 |
教学目标 | 1.通过学习英语句子的基本句法成分和结构,学会分析英语句子结构。 2.识别英语基本句法结构,对长度较长,内容较为丰富的英语句子能够做出正确的理解。 3.为英语句子写作奠定扎实的语法基础。 |
教学重点 | 识别并分析下面的句子结构:SV; SVO; SP; SV IO DO; SVOC; SVA; SVOA; There be … |
教学难点 | 能区别以下结构:SP与SVA;SVOC与SVOA; |
教学准备 |
|
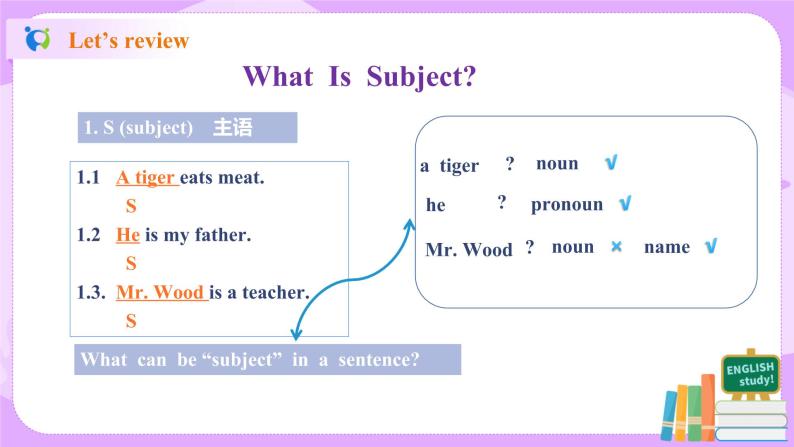
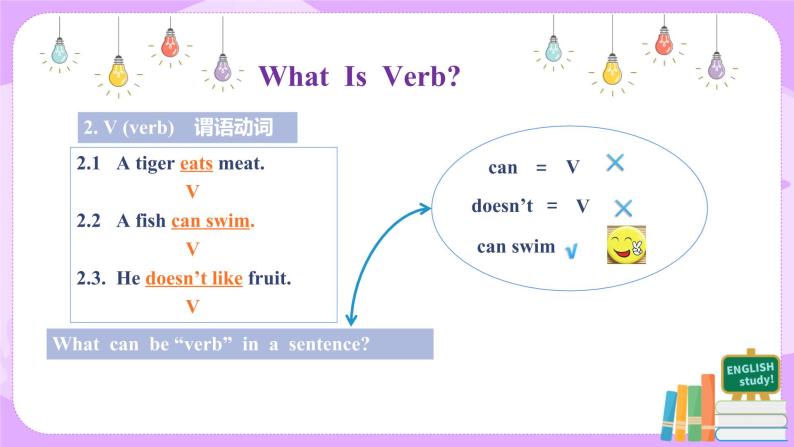
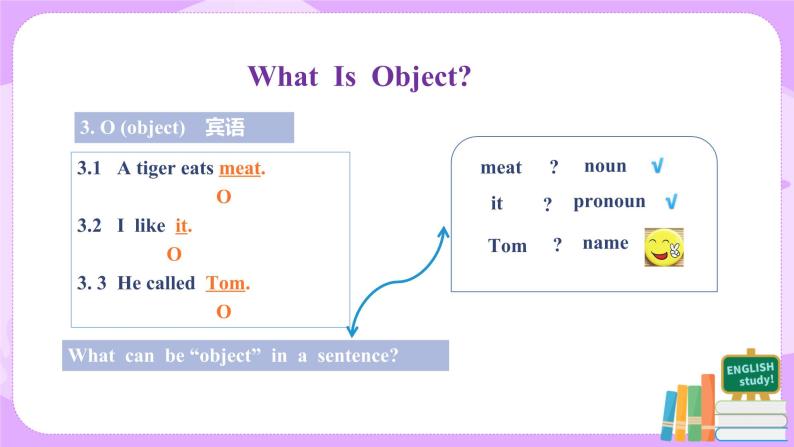
教学过程 | I Learn the technical terms-1. 1. S (subject) 主语 2. V (verb) 谓语动词 3. O (object) 宾语 4. P (predicative) 表语 5. A (adverbial) 状语 6. DO (direct objective) 直接宾语 7. IO (indirect objective) 间接宾语 8. C (objective complement) 宾语补足语 9. There be … there be结构 II Learn the technical terms-2. 1. What can be used as “Subject, Object, Predicative, Direct Object, Indirect Object and Ojective complement” in a sentence? 2. What can be used as “Adverbial” in a sentence? 3. What can be used as “verb” in a sentence?
Answers to questions 1-3: 1. Nouns, pronouns and appellations can be used as “Subject, Object, Predicative, Direct Object, Indirect Object and Ojective Complement”. Besides, adjectives can be used as “ Predicative and Ojective Complement” in a sentence. 2. Adverbs and prepositional phrases can be used as “Adverbial”. 3. Verbs with actual meaning can be used as “Verb” in a sentence. Auxiliary verbs alone cannot be used as “Verb” in a sentence.
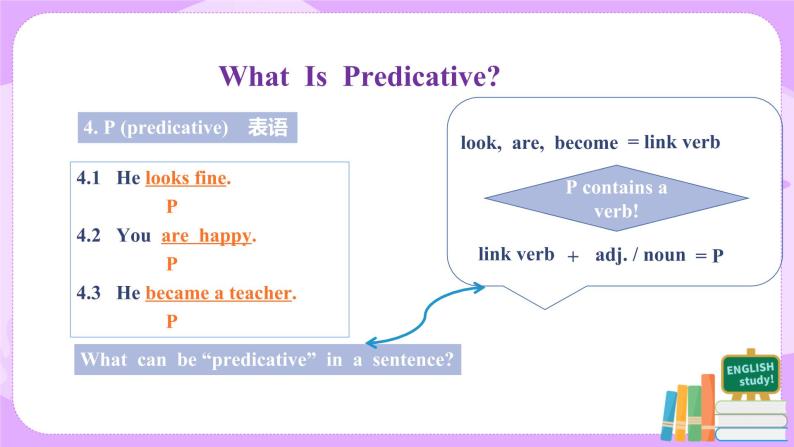
III Learn to recognize the sentence structures. 1. SV structure. For Example: (1) A bird flies. S V (2) A monkey jumps. S V (3) A fish swims. S V √ In SV structures, verbs are “intransitive verbs”. 2. SVO structure. For Example: (1) A sheep eats grass. S V O (2) They like bananas. S V O (3) He wants candy. S V O √ In SVO structures, verbs are “transitive verbs”. 3. SP structure. For Example: (1) This is great. S P (2) He looks well. S P (3) She became a teacher. S P √ In SP structures, Predicatives are formed by “link verbs” and “adjectives or nouns”. √ link verbs: be, become, grow, look, feel, taste, etc. 4. SV IO DO structure. For Example: (1) He asked me a question. S V IO DO
(2) Danny wrote me a letter. S V IO DO (3) Billy brought Sam a kite. S V IO DO √ In SV IO DO structures, the verbs are transitive and are followed by two objectives – pronouns or nouns as Indirect Objective, and nouns as Directi Objectives. √ verb pattern: tell sb. sth. 5. SVOC structure. For Example: (1) The war made him a hero. S V O C (2) They found the sanke dead. S V O C (3) We call him Mr. Wood. S V O C √ In SVOC structures, the verb is transitive and is followed by an objectives and a complement. The complement here is used to show the situation of the object. √ In SVOC structures, Objective complements can be nouns, adjectives, –ing phrases or –ed phrases. 6. SVA structure. For Example: (1) It rained heavily. S V A (2) He coughed badly. S V A (3) The rabbit ran fast. S V A √ In SVA structures, the verb is intransitive and is followed by an adverbial.
7. SVOA structure. For Example: (1) A sheep eats grass over there. S V O A (2) Mum makes lunch in the kitchen. S V O A (3) They liked the film very much. S V O A √ SVOA structure is formed by SVO structure plus an adverbial at the end.
8. There be structure. For Example: (1) There is an apple on the table. V S A (2) There are 7 days in a week. V S A
(3) There is milk and bread on the table. V S A √ In “There be…” structure, subject and verb “be” is inverted. √ The number of “Be” is decided by the very first subject followed.
IV Questions to think: 1. Look at the picture below and examine the sentence structures. What parts are shared by all of them?
2. In the eight basic structures, what is the more stable element and what is the most unstable element in a sentence?
V Read the sentences and analyse the structures. 1. The 100-year-old school lies in the center of S V A the city.
2. We must act. S V 3. The maths homework looks easy. S P 4. The teacher found the classroom empty. S V O C 5. My mum bought me a new dictionary. S V IO DO 6. Tom is looking forward to meeting the new S V O exchange studnent.
7. There is an English corner at our school. V S A 8. We had chemistry in the newly built lab. S V O A
VI Read the passage and analyse the structures of the underlined sentences. 1. That dream has come true! S P 2. Tim and his classmates are living on a ship. S V A 3. They also learn about ships and the sea. S V O 4. Tim writes his parents every week and tells S V O A V them what happened on the ship. IO DO 5. There’s always something exciting to do. V S
6. Studying and doing homework seem much more S P fun.
VII Answers to “IV Questions to think” 1. Each sentence shall have a “S” and a “V”. 2. “S” is relatively stable, compared to “V” - the most unstable part in English sentence.
Summary In this period, we’ve learned about some important concepts of syntax. 1. The definitions of “S (subject), V (verb), O (object), P (predicative), A (adverbial), DO (direct object), IO (Indirect object) and C (object complement)”; 2. The morphologic features correspongding to “ S (subject), V (verb), O (object), P (predicative), A (adverbial), DO (direct object), IO (Indirect object) and C (object complement)”; 3. “V”, as the most unstable part in English sentence, decides all the varieties of the basic sentence structures. 4. the importance of learning Verb patterns. Home work: 1. Recite the meanings of the capitalized initials “S (subject), V (verb), O (object), P (predicative), A (adverbial), DO (direct object), IO (Indirect object) and C (object complement)”. 2. Finish Ex. 2 and Ex. 3 on page 5 3. Think about the significance of distinguishing “transitive verbs” from “intransitive verbs”?
|
板书设计 | I What is What? 1. 1 What can be used as “Subject” in a sentence? 1.1.1 Nouns. For example: A tiger eats meat. S 1.1.2 Subject Pronouns. For example: He is a teacher. S 1.1.3 Appellations. For example: Mr. Wood is coming. S 1.2 What can be used as “Object” in a sentence? 1.2.1 Nouns. For example: A tiger eats meat. O 1.2.2 Object Pronouns. For example: I like him. O 1.2.3 Appellations. For example: We invite Mr. Wood. O 1.3 What can be used as “Predicative” in a sentence? 1.3.1 Link verb + adjective / noun. For exmaple: He is a teacher. This is great P P 1.3.2 Link verbs. For example: be, look, feel, tastes, smell, become, grow, etc. 1.4 What can be used as “Adverbial” in a sentence? 1.4.1 Preposition + a place. For example: in the room A 1.4.2 Preposition + time. For example: in 1918 A 1.4.3 Preposition + a traffic tool. For example: by bus A 1.4.3 Preposition + a noun. For example: with your help A 1.5 What can be used as “DO” in a sentence? 1.5.1 Nouns. For example: Give me the book. DO 1.5.2 Pronouns. For example: Pass them to me. DO 1.6 What can be used as “IO” in a sentence? 1.6.1 Pronouns. For example: Send him a letter. IO 1.6.2 Nouns. For example: Send my mum a letter. IO 1.6.3 Appellations. For example: Send Mr. Jin a letter. IO 1.7 What can be used as “C” in a sentence? 1.7.1 Adjectives. For example: It makes me happy. C √The implied logic between “me” and “happy” is “I am happy” 1.7.2 Nouns. For example: The war left him an orphan. C 1.7.3 –ing phrases. For example: He found it exciting. C 1.8 “There be …” is actually an inversion of “SV” or “SVA”. For example: 1.8.1 There is a boy in the room. V S A 1.8.2 There sits a boy. V S II Find the differences – SP vs. SVA 2.1. P in “SP” means “link. verb” + “adj. / noun” 2.2 VA means “intransitive verb”+ adverb 2.3 For example: look great P (link verb + adj.) work hard V A (vi. + adv.) III Find the differences – SVOC vs. SVOA 3.1 “C” means “nouns / adjectives.” 3.2 “A” means “adverbs / prepositional phrases” 3.3 For example: make him a hero / happy V O C miss you very much / in my heart V O A |
课后作业 | Homework 1. Recite the meanings of the capitalized initials “S (subject), V (verb), O (object), P (predicative), A (adverbial), DO (direct object), IO (Indirect object) and C (object complement)”. 2. Finish Ex. 2 and Ex. 3 on page 5 3. Think about the significance of distinguishing “transitive verbs” from “intransitive verbs”? |
人教版 (2019)必修 第一册Welcome unit精品ppt课件: 这是一份人教版 (2019)必修 第一册Welcome unit精品ppt课件,文件包含welcomeunit第4课时课件PPTppt、welcomeunit第4课时练习课件PPTppt等2份课件配套教学资源,其中PPT共57页, 欢迎下载使用。
人教版 (2019)必修 第一册Welcome unit精品ppt课件: 这是一份人教版 (2019)必修 第一册Welcome unit精品ppt课件,文件包含welcomeunit第3课时练习课件PPTppt、welcomeunit第3课时课件PPTppt等2份课件配套教学资源,其中PPT共54页, 欢迎下载使用。
高中英语人教版 (2019)必修 第一册Welcome unit优质ppt课件: 这是一份高中英语人教版 (2019)必修 第一册Welcome unit优质ppt课件,文件包含welcomeunit第2课时课件PPTppt、welcomeunit第2课时练习课件PPTppt等2份课件配套教学资源,其中PPT共81页, 欢迎下载使用。